
Pea protein is a high-quality, plant-based protein extracted from yellow peas. [1] It’s processed to isolate or concentrate the protein, offering a clean, allergen-free nutrition source. Popular in the health and wellness industry, pea protein fits the various dietary needs, including vegan, vegetarian, and hypoallergenic diets.
Pea protein is highly digestible with a Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) close to 1.0, meaning it's easily absorbed. [2]
It’s a complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids, which is rare among plant-based proteins. It’s non-GMO, cholesterol-free, and low in saturated fats, making it a heart-healthy, sustainable option. With its balanced amino acid profile, high iron content, and eco-friendly nature, pea protein is ideal for health-conscious individuals and athletes.
Pea protein is present in the Miduty Shape Me Up Supplement. When it comes to plant-based protein, pea protein is often overlooked despite its exceptional benefits.
Miduty’s Pea Protein stands out by providing a full spectrum of essential amino acids, including methionine, often lacking in other plant-based proteins. This makes it a complete protein source, perfect for muscle repair, growth, and other body functions.
It is purity tested to ensure high quality, highly bioavailable for better absorption, and is combined with FOS (fructooligosaccharides) to support gut health and enhance digestion.
Pea protein is known for its excellent digestibility compared to other plant proteins, such as soy or wheat. It’s gentle on the stomach and less likely to cause bloating, making it perfect for individuals with digestive sensitivities or those prone to gastrointestinal discomfort.
Pea protein is naturally free from gluten, dairy, soy, and other common allergens, making it an excellent choice for individuals with food sensitivities or allergies. This makes Miduty's Pea Protein a versatile option for a wide range of diets.
| Uses & Benefits | Description |
| Supports Muscle Growth and Repair | Pea protein is a complete protein with all nine essential amino acids for muscle repair and growth. Consuming it after exercise helps muscle recovery by providing key building blocks. Amino acids like leucine stimulate muscle protein synthesis, reducing soreness. [3] Studies show pea protein can help prevent age-related muscle loss in older adults, making it ideal for seniors who want to maintain muscle mass without digestive issues from dairy-based proteins. [4] |
| Promotes Weight Management | Pea protein helps increase feelings of fullness, reducing calorie intake. Its protein and fiber content curb hunger, making it a great choice for weight management and reducing cravings. By boosting metabolism and slowing carb conversion into fat, pea protein supports weight loss while preserving lean muscle. [5] Naturally low in fat, it offers a balanced macronutrient profile, making it ideal for those focused on weight control. |
| Supports Heart Health | Pea protein can help lower blood pressure, especially in those with high levels. It may release molecules that relax blood vessels and improve circulation. Studies show it reduces LDL (bad) cholesterol, total cholesterol, and improves lipid profiles, lowering the risk of heart disease and stroke. [6] It also contains antioxidants that protect the heart from oxidative stress and amino acids that reduce inflammation and support heart health. |
| Enhances Digestion and Gut Health | Pea protein contains fiber that aids digestion by promoting healthy bowel movements and preventing constipation. [7] It also supports a healthy gut microbiome, stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria. This improves digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall gut health. Unlike some plant proteins, pea protein is gentle on the stomach and easy to digest, without causing bloating or gas. |
| Promotes Healthy Skin, Hair, and Nails | Pea protein supports collagen production, which helps reduce wrinkles and fine lines for youthful skin. Collagen also strengthens hair and nails. It contains biotin, a B-vitamin that promotes hair growth, and cysteine, which helps produce glutathione, an antioxidant that supports healthy skin. The antioxidants in pea protein can reduce skin inflammation, helping with conditions like acne and eczema, leading to clearer, healthier skin. [8][9] |
| Ideal for Vegan and Vegetarian Diets | Pea protein is a great option for vegans and vegetarians who may struggle to get enough protein. Unlike soy, it’s free from common allergens, making it suitable for various diets. Pea protein is a complete protein, providing all nine essential amino acids, which are important for muscle growth, tissue repair, and overall health. |
| Blood Sugar Regulation | Pea protein can help regulate blood sugar by improving insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes or at risk. [10] With a low glycemic index, it has minimal impact on blood sugar, making it a great choice for managing glucose levels. |
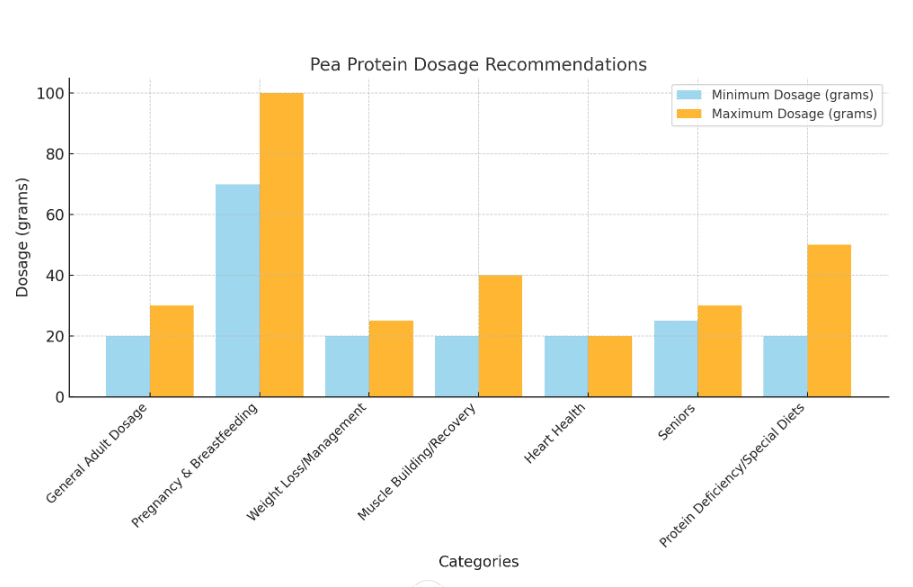
The adequate dosage of Pea Protein can vary depending on age, health status, and specific needs.
General Adult Dosage: 20–30 grams per day is sufficient for individuals looking to meet their daily protein requirements or maintain a balanced diet.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Protein needs typically increase during pregnancy and breastfeeding to support the health of both mother and baby. However, the specific amount will depend on dietary intake and individual requirements. Generally, pregnant women may need 70–100 grams of protein daily, including sources like pea protein.
Specific Health Conditions:
For Weight Loss or Management: 20–25 grams per serving, taken as a meal replacement or snack, helps curb hunger by promoting satiety.
For Muscle Building and Recovery: 20–40 grams per serving, consumed post-workout or as part of meals, can support muscle repair and growth. This amount aligns with research suggesting 0.8–2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily for active individuals.
For Heart Health: Regular intake of 20 grams per day may help lower cholesterol and improve heart health, as shown in some studies.
For Seniors: Older adults may benefit from 25–30 grams per meal to counteract age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia).
For Protein Deficiency or Special Diets: Pea protein can supplement dietary intake for individuals with limited access to other protein sources. Dosage may range from 20–50 grams daily, depending on the gap in dietary protein.
Post-Workout (For Muscle Recovery and Growth): Within 30–60 minutes after exercise. The body is in a heightened state of protein synthesis post-workout. Pea protein's rich branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) content supports muscle repair and recovery.
Morning (For General Health and Energy): During breakfast or as part of a morning smoothie. Provides a sustained release of amino acids, keeping you energized throughout the day. Supports muscle maintenance and curbs mid-morning cravings.
Between Meals (For Appetite Control and Weight Management): As a mid-morning or mid-afternoon snack. Pea protein increases satiety and reduces hunger, helping to control calorie intake. Balances blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes.
Before Bed (For Muscle Repair During Sleep): 30 minutes before bedtime. Provides a slow release of amino acids to support overnight muscle repair and recovery. May prevent muscle breakdown during fasting periods (e.g., overnight).
Pre-Workout (For Energy and Endurance): 1–2 hours before exercise. Supplies amino acids to fuel workouts and prevent muscle breakdown. Helps maintain stamina and focus during exercise.
Digestive Issues: Pea protein contains natural compounds like oligosaccharides, which may ferment in the gut. Bloating, gas, or mild stomach discomfort, especially in individuals with sensitive digestion or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Potential Allergies: While rare, some individuals may have allergies to peas or legumes. Skin rashes, itching, or respiratory issues.
Risk of Excessive Protein Intake: Over-consuming protein, including pea protein, can strain kidneys or liver, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions. Nausea, dehydration, or fatigue from excessive nitrogen waste in the body.
Stay Hydrated: Protein metabolism increases water requirements. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support kidney function.
Pea protein is a highly nutritious, plant-based protein that offers a complete amino acid profile, making it ideal for muscle growth and repair. It's easily digestible, making it suitable for those with sensitivities to other protein sources. Beyond muscle support, pea protein promotes weight management by increasing satiety and supporting lean muscle mass.
Its heart-healthy benefits, such as lowering blood pressure and improving cholesterol levels, contribute to overall cardiovascular health.
Additionally, pea protein enhances digestion, supports healthy skin, hair, and nails, and is a great choice for vegans, vegetarians, and those with dietary restrictions. It's a versatile, sustainable, and allergy-friendly option for anyone seeking a high-quality protein.
| Sr. No. | Reference |
|---|---|
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. | Protein Source and Muscle Health in Older Adults: A Literature Review - PMC |
| 5. | A high-protein diet for reducing body fat: mechanisms and possible caveats - PMC |
| 6. | |
| 7. | |
| 8. | |
| 9. | |
| 10. |
